Sukuk as an Asset in Your Portfolio
Sukuk are considered one of the investment debt instruments, defined as equal-value financial certificates representing common shares in an existing asset or one to be created from the subscription proceeds, and they comply with Islamic Sharia.
So, what distinguishes debt instruments?
And what is their impact on the investment portfolio?
Debt instruments differ from stocks in their structure, returns, and legal considerations. Debt instruments are characterized by a fixed period for repaying the principal amount along with an agreed-upon schedule for periodic payments, enabling investors to calculate their returns and predict their profits.
An investor in stocks owns a share in the company, while an investor in debt instruments is considered a creditor to the company, whose relationship ends upon receiving their dues. Therefore, investing in debt instruments generally carries less risk than stocks.
When making investment decisions, diversification among assets must be considered. Diversification is a method to reduce risks by allocating investments across various financial instruments that react differently to the same event.
Each asset has characteristics different from the other portfolio components in terms of volatility—meaning risk and returns. At a given time, one asset class may lead the market while others lag behind, but in a diversified portfolio, a decline in one asset is often offset by growth and gains in another.
Debt instruments play an equally important role as other assets, providing relative stability through regular returns at best, and priority claims in case of debtor bankruptcy at worst.
There are various types of debt instruments, including bonds, treasury bills, and sukuk. The latter is distinguished by its compliance with Islamic Sharia, offering investors predetermined periodic payments and the benefits of investment diversification.
The following scenarios illustrate the impact of debt instruments in a portfolio:
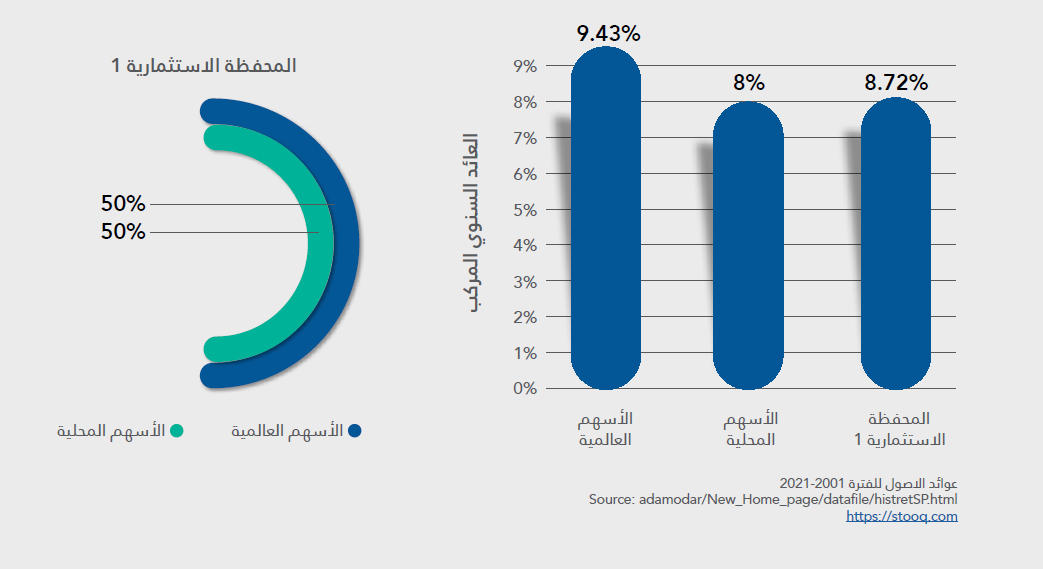
First scene
The first scenario shows an investment portfolio consisting of stocks only. It demonstrates high returns compared to other investment portfolios. However, since the portfolio contains only stocks—even if diversified across local and global markets—its risks remain very high.
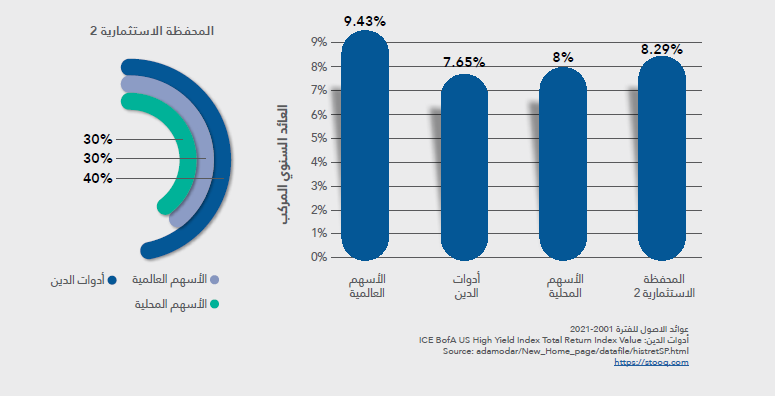
Second scene
The second scenario shows a portfolio consisting of both stocks and debt instruments. Debt instruments help maintain high returns but with lower risks, as shown in Figure (4), which illustrates the portfolio's risk level.
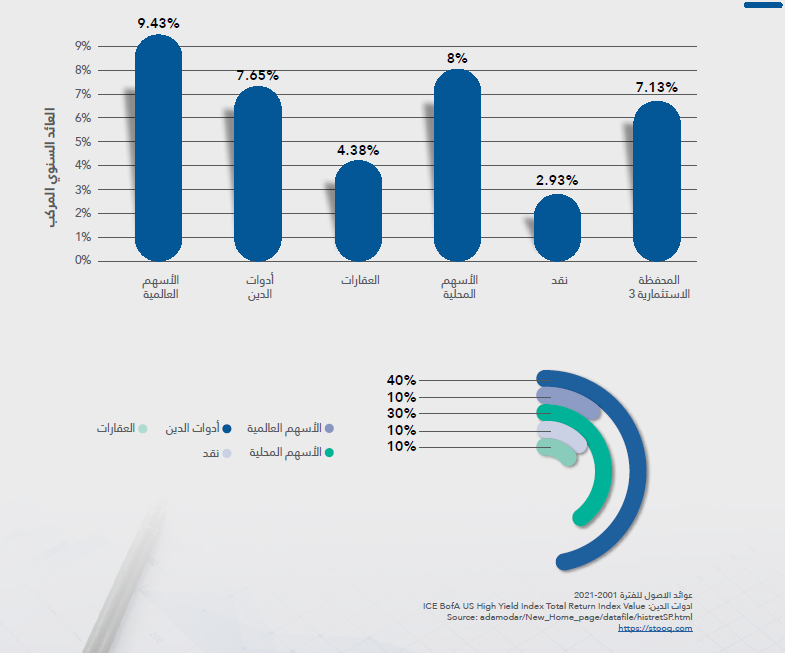
Third scene
In the third scenario, the investment portfolio consists of five asset classes divided as shown in the following chart. Due to the increased diversification of assets, risks decreased compared to the second portfolio, although returns also decreased because the added assets (cash and real estate) typically do not yield high returns.
Finally, when comparing the three investment portfolios, the impact of diversification becomes evident in preserving returns while reducing investment risks, measured by standard deviation. The standard deviation is a measure of dispersion—high volatility in either direction raises the standard deviation of the asset or portfolio, thereby increasing risk.
The following table shows the annual compound return and standard deviation of the investment portfolios for the period (2001–2021):
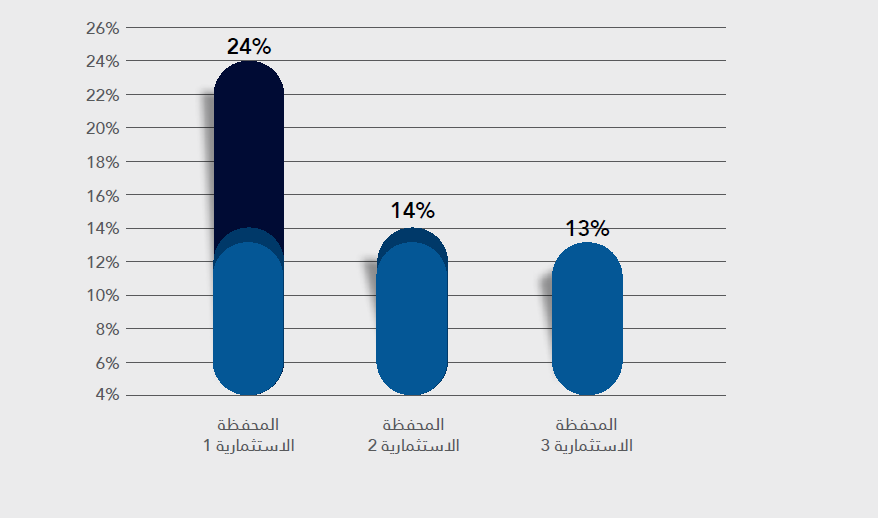
Dangers
The chart below illustrates the risks of the investment portfolios. Naturally, Portfolio 1 is the riskiest because, as mentioned earlier, it contains only one asset—stocks. Next comes Portfolio 2, which significantly reduced risks by adding debt instruments. Portfolio 3 is not far behind Portfolio 2 in terms of risk since it also diversified its asset composition.









